os-lab6-challenge
challenge-6
梳理本challenge中重要的函数及实现的修改
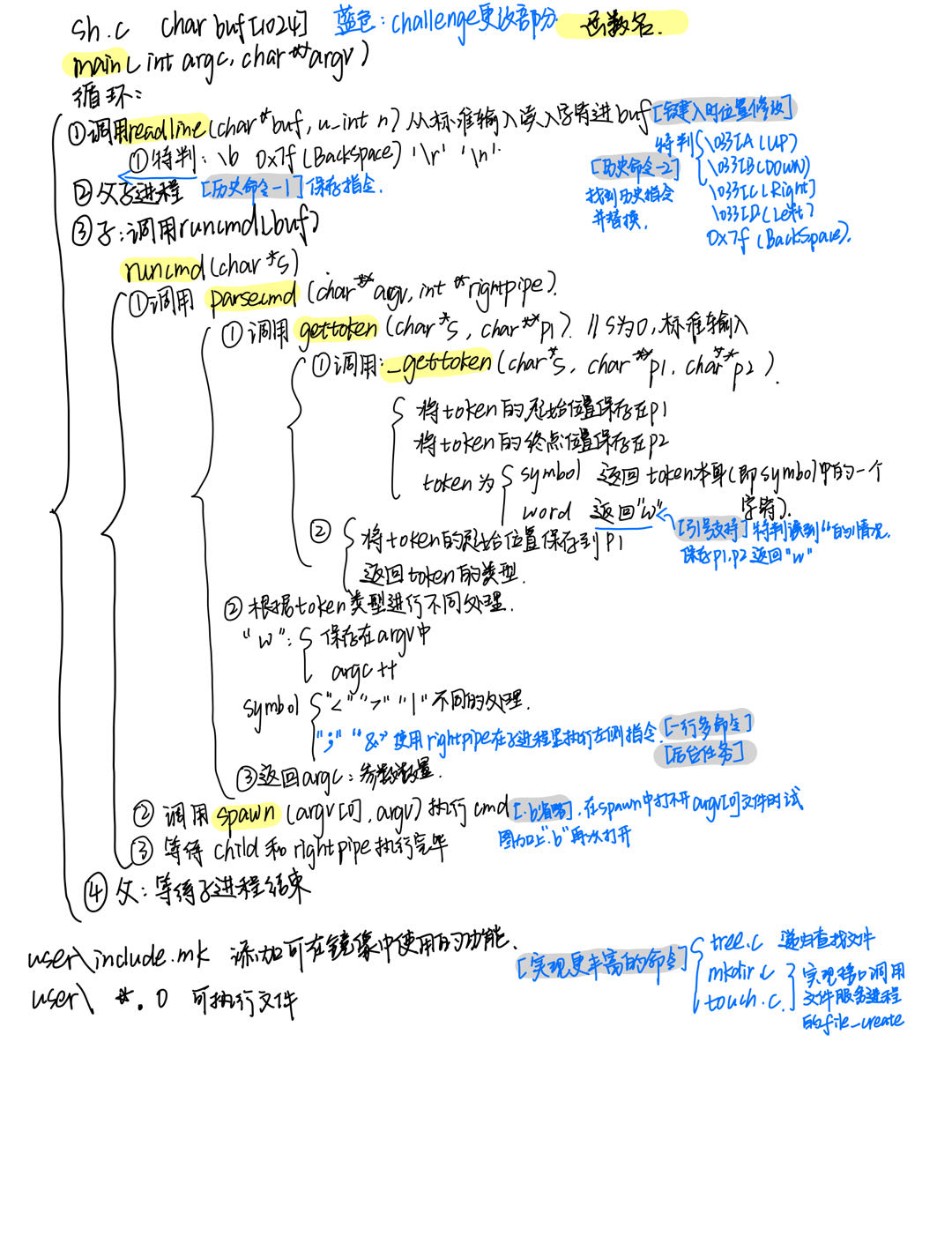
必做部分-easy
实现一行多命令
用 ; 分开同一行内的两条命令,表示依次执行前后两条命令。; 左右的命令都可以为空。
提示:在 user/sh.c 中的保留 SYMBOLS 里已经预留有 ; 字符。
解决方法
1 | //sh.c parsecmd |
左侧指令:子进程,直接返回参数
右侧指令:父进程,在子进程执行完毕之后继续解析
实现后台任务
用 & 分开同一行内的两条命令,表示同时执行前后两条命令。& 左侧的命令应被置于后台执行,Shell 只等待 & 右侧的命令执行完毕,然后继续执行后续语句,此时用户可以输入新的命令,并且可能同时观察到后台任务的输出。你需要自行设计测试,以展现此功能的运行效果。& 左侧的命令不能为空。
提示:在 user/sh.c中的保留 SYMBOLS 里已经预留有 & 字符
解决办法
1 | case '&': |
由于runcmd函数只等待child和rightpipe执行结束才能完成,所以不会等待左侧命令执行
实现引号支持
实现引号支持后,shell 可以处理如: echo.b "ls.b | cat.b" 这样的命令。即 shell 在解析时,会将双引号内的内容看作单个字符串,将 ls.b | cat.b 作为一个参数传递给 echo.b。
1 | //user/sh.c _gettoken |
修改_gettoken函数,在识别到引号的时候返回引号内的一整个字符串(即将p1修改为引号内字符串开始的位置,p2修改为引号内字符串结束的位置)
实现程序名称中 .b 的省略
目前的用户程序被烧录到文件系统中后,其可执行文件以 .b 为后缀,为 shell 中命令的输入带来了不便。你需要修改现有的实现,以允许命令中的程序名称省略 .b 后缀,例如当用户指定的程序路径不存在时,尝试在路径后追加 .b 再打开。
1 | //user/lib/spawn.c spawn |
尝试加入”.b”再次打开
如果再次打开仍然失败返回错误
必做部分-hard
实现键入命令时任意位置的修改
现有的 shell 不支持在输入命令时移动光标。你需要实现:键入命令时,可以使用 Left 和 Right 移动光标位置,并可以在当前光标位置进行字符的增加与删除。要求每次在不同位置键入后,可以完整回显修改后的命令,并且键入回车后可以正常运行修改后的命令。
上下左右
1 | // UP: \033[A |
特判:
Backspace
刷新输入框
- 光标左移
- printf
- 光标左移
1
2
3
4
5// 举例 删除最后一个字符 刷新
buf[--i] = 0;
MOVELEFT(1);
printf(" ");
MOVELEFT(1);光标i之后的字符前移
左右箭头
- 光标变化
- 维持i与光标的关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15if (temp2 == 'D')
{
// 左移
if (i > 0)
{
i -= 1;
//维持i的值与光标的位置一致
}
else
{
MOVERIGHT(1);
//抵消
}
}
//右移同理上下箭头
- 见history一节
实现更丰富的命令
参考实验环境中的 Linux 命令 tree、mkdir、touch 来实现这三个命令,请尽可能地实现其完整的功能。
为了实现文件和目录的创建,你需要实现用户库函数 mkdir() 和文件打开模式 O_CREAT。
实现文件的创建后,你需要修改 shell 中输出重定向 > 的实现,使其能够在目标路径不存在时自动创建并写入该文件。
tree
参考ls.c实现
注意:
- 在tree命令最后要输出目录数量 + 文件数量
- tree命令可以有不止一个参数,同时显示多个目录相关信息
相关函数:
stat:粗略理解为打开文件,返回统计信息
1 | struct Stat { |
1 | //在linux系统下使用tree命令截取一段作为对照进行实现 |
1 | //treedir |
判断是目录最后一个文件(需要输出
printf("└── ");而不是printf("├── ");1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37//tree.c treedir
void treedir(char *path, int depth)
{
int fdnum;
struct Fd *fd;
struct Filefd *ffd;
int n;
//struct File f;
//struct File pref;
// open
if ((fdnum = open(path, O_RDONLY)) < 0)
{
user_panic("open %s: %d", path, fdnum);
}
fd = (struct Fd *)num2fd(fdnum);
ffd = (struct Filefd *)fd;
int size = ffd->f_file.f_size;
int va = (int)fd2data(fd);
for(int i = 0; i < size; i += BY2FILE){
struct File *file;
file = (struct File*)(va + i);
if(file -> f_name[0] == 0){
break;
}
int islast = 0;
if(i == size || (file + 1)->f_name[0] == 0){
islast = 1;
}
treefile(path, file->f_type == FTYPE_DIR, file->f_name, depth + 1,islast);
}
}
//treefile
if(islast){
printf("└── ");
} else {
printf("├── ");
}对目录的蓝色显示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15//-f需要输出完整命令
if (flag['f'] && path)
{
if(isdir){
printf("\033[0;34m%s\033[0m", path);
printf("\033[0;34m%s\033[0m", sep);
} else {
printf("%s%s", path, sep);
}
}
if(isdir){
printf("\033[0;34m%s\033[0m\n", name);
} else {
printf("%s\n", name);
}
基本思路
- main
- tree:打开文件
- treedir:对目录执行tree,对目录的子文件调用treefile
- treefile(如果判断为isdir会调用treedir
- treedir:对目录执行tree,对目录的子文件调用treefile
- tree:打开文件
mkdir && touch
实现文件创建功能——实现调用链调用文件进程中的file_create()
参考已有调用实现
- 用户进程
int fsipc_create(const char *, int);int create(const char *path, int f_type);
- 文件进程
int file_create(char *path, struct File **file);
历史命令
- 在sh.c的main函数readline之后中增加保存指令功能
- 在readline函数中增加对\033[A和\033[B的特判
我的实现
保存历史指令
原本:(后来仔细看指导书发现是禁止的)
1
2static char history[1000][128];//循环保存最近的1000条指令
static int k = 0;//记录下一个指令在数组中的位置更改:(但是这个方法出现了一些bug)
增加O_APPEND
新建/.history文件保存历史指令
static int init_history = 0标志是否已经创建history文件void savecmd(char * buf)保存int getcmd(int index, char *ans)读取
readline上下键特判
UP
index == k 保存当前已经输入的内容到
static char curcmd[1024];index > 0
抵消输入的UP
MOVEDOWN(1);更改index
index--;更改显示
1
2
3
4
5
6MOVELEFT(i);
for(int j = 0; j < len; j++){
printf(" ");
}
MOVELEFT(i);
printf("%s",history[index]);更改buf
1
2
3
4
5len = strlen(history[index]);
for(int j = 0; j < len; j++){
buf[j] = history[index][j];
}
i = len;
DOWN
- 与UP类似
- 差别在:
- index == k-1 用curcmd替换
遇见的bug:主要还是逻辑错误,比如应该if-else的分支使用了if-if
history指令:显示所有历史指令
选做:支持相对路径
改变进程控制块
1
2
3struct Env {
char r_path[256];
};增加系统调用
- SYS_getRpath 获得相对路径
- SYS_setRpath 改变相对路径
pwd指令
拼装相对路径或绝对路径的逻辑,分为以下几类
- 绝对路径
- 以../开头的相对路径
- 以./开头的相对路径
- 以文件名开头的相对路径
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90//cd
if(buf[0]=='c' && buf[1] == 'd' && buf[2] == ' '){
//test
//syscall_setRpath("/kern/test");
char cur[1024] = {0};
char dst[1024];//存储cd的参数
char dir[1024] = {0};
char *pdst = dst;
int i = 3;
int j = 0;
while(buf[i] != 0 && buf[i] != '\n' && buf[i] != '\r'){
if(buf[i] == ' '){
i++;
continue;
} else {
dst[j++] = buf[i];
i++;
}
}
dst[j] = 0;
//printf("%s\n",dst);
syscall_getRpath(cur);
int lencur = strlen(cur);
int lendst = strlen(dst);
if(dst[0] == '/'){
//绝对路径
strcpy(dir,dst);
} else if(dst[0] == '.' && dst[1] == '.'){
//以../开头的相对路径
char pre[1024];
int m;
int len_m;
for(m = lencur-1;m >=0;m--){
if(cur[m] == '/'){
break;
}
}
if(m == 0){
pre[0] = '/';
pre[1] = 0;
len_m = 1;
} else {
len_m = m + 1;
pre[m+1] = 0;
pre[m] = '/';
m--;
for(;m>=0;m--){
pre[m] = cur[m];
}
}
strcpy(pre + len_m,dst + 3);
strcpy(dir,pre);
} else if(dst[0] == '.'){
//以./开头的相对路径
pdst += 2;
if(strcmp(cur,"/") != 0){
strcpy(cur + lencur,"/");
strcpy(cur + lencur + 1,pdst);
} else {
strcpy(cur + lencur,pdst);
}
strcpy(dir,cur);
} else{
//以文件名开头的相对路径
if(strcmp(cur,"/") != 0){
strcpy(cur + lencur,"/");
strcpy(cur + lencur + 1,dst);
} else {
strcpy(cur + lencur,dst);
}
strcpy(dir,cur);
}
printf("%s\n",dir);
//dir为拼好的绝对路径
struct Stat st;
if((r = stat(dir,&st)) < 0){
printf("bug1\n");
exit();
}
//bug:明明是dir却输出不是dir
// if(!st->st_isdir){
// printf("not a dir");
// continue;
// }
if(!st.st_isdir){
printf("not a dir");
continue;
}
chdir(dir);
continue;bug:明明是dir却输出不是dir
”指针错误“
除了cd部分需要拼装以支持相对路径的地方
用户态的open函数
- 在file.c里新建函数
void changePath(const char *dst, char *dir)基本是上述代码逻辑
- 在file.c里新建函数
ls(调用
void changePath(const char *dst, char *dir)tree(同上)
touch(改为在当前目录中创建)
mkdir(改为在当前目录中创建)
spawn
- 防止把指令prog解释为相对路径
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14int spawn(char *preprog, char **argv) {
// Step 1: Open the file 'prog' (the path of the program).
// Return the error if 'open' fails.
int fd;
char prog[1024];
char *pprog = prog;
if(preprog[0] != '/'){
prog[0] = '/';
strcpy(pprog + 1, preprog);
} else {
strcpy(prog,preprog);
}
if ((fd = open(prog, O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
//...
测试
1 | #测试一行多命令 |
最后的结果
1 | tree -f |